Steel Siding Cost A Comprehensive Guide
Steel siding cost is a crucial factor for homeowners considering this durable and aesthetically pleasing exterior cladding. This guide delves into the multifaceted aspects influencing the overall expense, from material selection and labor costs to regional price variations and project complexity. We’ll dissect the price differences between various steel siding types, compare it to alternatives like vinyl and wood, and equip you with the knowledge to create a realistic budget for your project. Understanding the complete picture of steel siding cost is key to making an informed decision.
We’ll explore the intricacies of installation costs, including hidden expenses and how factors like roofline complexity impact the final bill. We’ll provide practical methods for estimating costs, creating a detailed budget, and leveraging online resources for accurate pricing. By the end, you’ll be armed with the knowledge to confidently navigate the world of steel siding pricing and choose the best option for your home.
Factors Influencing Steel Siding Cost
The price of steel siding installation isn’t a one-size-fits-all proposition. Several key factors interact to determine the final cost, ranging from the type of steel used to the size and complexity of your project. Understanding these variables is crucial for accurate budgeting and informed decision-making.
Material Quality and Type
Steel siding comes in various grades and finishes, directly impacting the cost. Higher-grade steel offers superior durability and longevity, translating to a higher upfront price but potentially lower long-term costs due to reduced maintenance and replacement needs. For instance, galvanized steel, while more affordable than painted steel, offers excellent corrosion resistance, making it a budget-friendly option in many climates. Painted steel, on the other hand, boasts a wider array of colors and finishes, enhancing curb appeal but adding to the initial expense. The thickness of the steel is another critical factor; thicker steel is more resistant to dents and damage but comes with a higher price tag.
Labor Costs and Regional Variations
Labor costs are a significant component of the overall expense. These costs vary considerably depending on your location. Areas with a high cost of living or a shortage of skilled labor will naturally have higher installation fees. The complexity of the installation also plays a role; projects requiring extensive preparation work, such as removing existing siding or dealing with intricate architectural details, will command higher labor costs. For example, a simple installation on a rectangular house will be less expensive than one involving numerous dormers, gables, or complex trim work.
Project Size and Complexity, Steel siding cost
The size of your house directly correlates with the amount of material needed and the labor hours required. Larger houses inherently demand more steel siding and more installation time, leading to higher costs. Beyond size, the complexity of the project significantly impacts the final price. A house with many angles, dormers, or other architectural features will require more precise cuts and extra time for installation, increasing both material and labor costs. For instance, a simple ranch-style home will be less expensive to side than a Victorian-style house with numerous intricate details.
Cost Comparison Table
The following table provides a general estimate of steel siding costs per square foot. Remember that these are averages and actual costs can vary based on the factors discussed above.
| Siding Type | Cost per Square Foot (Material) | Cost per Square Foot (Installation) | Total Cost per Square Foot |
|---|---|---|---|
| Galvanized Steel | $1.50 – $3.00 | $3.00 – $6.00 | $4.50 – $9.00 |
| Painted Steel | $2.50 – $5.00 | $4.00 – $7.00 | $6.50 – $12.00 |
| High-End Steel (e.g., with extra features) | $4.00 – $8.00 | $6.00 – $10.00 | $10.00 – $18.00 |
Steel Siding vs. Other Materials

Choosing the right exterior siding is a crucial decision impacting both the aesthetics and longevity of your home. While steel siding offers several compelling advantages, it’s essential to compare its cost and performance against other popular options like vinyl, wood, and aluminum to make an informed choice. This comparison will consider initial costs, long-term maintenance, and overall lifespan to determine the most cost-effective solution over time.
Cost Comparison of Steel, Vinyl, and Wood Siding
The initial cost of siding varies significantly depending on the material, quality, and installation complexity. Steel siding typically falls in the mid-range, more expensive than vinyl but less costly than high-end wood options. However, the true cost picture emerges when factoring in maintenance and longevity. Over a 20-year period, the seemingly cheaper initial investment in vinyl or even wood might be offset by higher maintenance costs and shorter lifespan.
Long-Term Cost-Effectiveness
Steel siding’s strength lies in its durability and low maintenance requirements. Unlike wood, which is susceptible to rot, insect infestation, and requires regular painting or staining, steel siding resists these issues. Vinyl siding, while relatively low-maintenance, can crack, fade, or become brittle over time, potentially necessitating replacements sooner than steel. This inherent durability translates to lower long-term costs, as fewer repairs and replacements are needed. For instance, a home in a coastal area prone to harsh weather would see significant cost savings with steel siding compared to wood due to the latter’s susceptibility to moisture damage.
Key Cost Advantages and Disadvantages
Steel siding offers several key cost advantages, including: lower long-term maintenance costs, increased home value due to its durability, and potentially lower insurance premiums due to its fire resistance. However, the initial cost might be higher than vinyl, and professional installation is generally recommended, adding to the overall expense. The potential for dents or scratches should also be considered, though high-quality steel siding is designed to withstand impact. Compared to wood, steel offers superior longevity and lower maintenance but may lack the aesthetic appeal of certain wood styles for some homeowners. Aluminum siding offers similar low maintenance to steel, but often lacks the strength and durability.
Twenty-Year Cost Comparison
The following table illustrates a hypothetical cost comparison over 20 years for three siding materials: steel, vinyl, and wood. These figures are estimates and can vary based on location, material quality, labor costs, and specific home characteristics. It’s crucial to obtain personalized quotes from contractors for accurate cost projections.
| Material | Initial Cost | Annual Maintenance | Total Cost (20 years) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | $15,000 | $100 | $17,000 |
| Vinyl | $8,000 | $200 | $12,000 |
| Wood | $20,000 | $500 | $30,000 |
Breakdown of Installation Costs
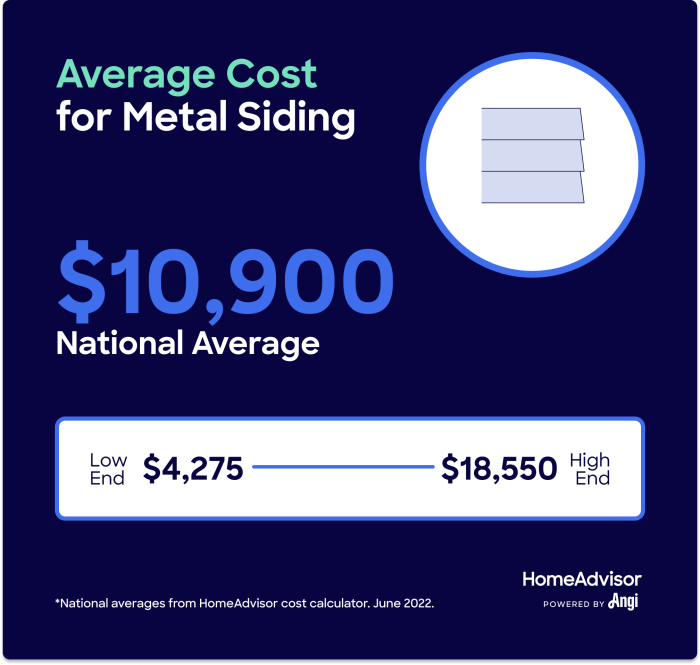
Steel siding installation costs are more than just the price of the material itself. A comprehensive understanding of the various contributing factors is crucial for accurate budgeting and avoiding unexpected expenses. This section details a typical cost breakdown, highlighting potential hidden costs and the influence of project specifics.
The total cost of a steel siding installation is a sum of several key components. These components can vary significantly depending on the size of the project, the complexity of the installation, and your geographic location. Understanding each element allows for more accurate cost projections and informed decision-making.
Labor Costs
Labor costs represent a significant portion of the overall expense. The hourly rate for experienced siding installers varies regionally, but expect to pay anywhere from $30 to $75 per hour, depending on experience and location. The total labor cost will depend on the size of your home, the complexity of the installation (e.g., multiple stories, intricate rooflines), and the installer’s efficiency. For a 2,000 square foot home, labor could range from $3,000 to $15,000 or more. This variation emphasizes the importance of obtaining multiple quotes from reputable installers.
Material Costs (Beyond Siding)
While the steel siding itself is a major expense, other materials are also necessary for a complete installation. These include: fasteners (nails, screws), flashing (to prevent water penetration around windows and doors), trim (to finish the edges of the siding), and sealant (to ensure a watertight seal). These supplementary materials can add several hundred to several thousand dollars to the overall cost, depending on the project’s scale and complexity. For instance, a complex roofline might necessitate more flashing and trim, driving up material costs.
Permits and Inspections
Building permits are often required for exterior renovations, including steel siding installation. Permit fees vary widely by location, ranging from a few hundred dollars to over a thousand dollars depending on the local regulations and the project’s size. Inspections are also typically mandated at various stages of the installation process, potentially adding additional costs. Failing to obtain the necessary permits can lead to fines and delays, making it a critical aspect of the budgeting process.
Hidden or Unexpected Costs
Several hidden or unexpected costs can significantly impact the final budget. These include:
- Existing Siding Removal: Removing old siding, especially if it’s difficult to access or made of materials like asbestos, can add considerable time and expense to the project. The cost of disposal of old siding also needs to be factored in.
- Repair of Underlying Structure: During the installation process, underlying issues such as rotted wood or damaged sheathing may be discovered. Repairing these problems adds to the overall cost and extends the project timeline. For example, discovering extensive rot under vinyl siding during removal could increase costs by several thousand dollars.
- Unexpected Material Needs: Accurate material estimations are crucial. However, unforeseen circumstances may require additional materials, increasing the final cost. This could involve needing more flashing due to unexpected gaps or needing to replace damaged sections of underlying structure.
- Site Conditions: Difficult access to the property, such as steep slopes or limited space for equipment, may increase labor costs as it will take longer to complete the job.
Impact of Roofline Complexity and Existing Siding Removal
The complexity of your roofline significantly impacts installation time and material costs. Intricate designs with many angles and valleys require more precise cuts and more flashing, increasing both labor and material expenses. Similarly, the removal of existing siding, particularly older or more difficult-to-remove materials, adds considerable time and labor to the project, leading to a higher overall cost. For example, removing asbestos siding requires specialized contractors and disposal methods, adding substantially to the cost.
Estimating and Budgeting for Steel Siding
Accurately estimating the cost of steel siding is crucial for successful project planning and execution. Underestimating can lead to budget overruns and project delays, while overestimating might lead to missed opportunities. A well-defined budget, incorporating realistic cost estimates and contingency planning, is essential for managing your steel siding project effectively.
Methods for Accurate Cost Estimation
Several methods exist for accurately estimating the cost of steel siding. The most common approach involves calculating the total square footage of the area to be sided, then multiplying that figure by the cost per square foot of the chosen material and installation. This requires detailed measurements of your home’s exterior walls, including any complexities like dormers, gables, or multiple stories. Remember to factor in waste – typically 5-10% – to account for cuts and imperfections. You should also consider the cost of accessories like trim, flashing, and fasteners. A more precise estimation can be obtained by breaking down the project into smaller, manageable components, estimating each individually, and summing the results. For example, separately estimating the costs for materials, labor, permits, and contingency funds provides a more detailed and accurate overall cost.
Creating a Realistic Budget with Contingency
A realistic budget goes beyond simply estimating the material and labor costs. It must incorporate several other critical components. A contingency fund is paramount; it accounts for unforeseen expenses, such as material price fluctuations, unexpected repairs, or labor cost increases. A well-defined budget should allocate at least 10-15% of the total estimated cost to this contingency fund. For example, if the initial estimate is $10,000, a contingency fund of $1,000-$1,500 should be included. This buffer provides financial protection against unexpected events, ensuring the project remains on track without significant financial strain.
Utilizing Online Calculators and Contractor Consultations
Numerous online cost calculators provide preliminary estimates for steel siding projects. These tools typically require inputting basic project details, such as the house’s dimensions and the chosen siding type. While convenient, these calculators often provide only rough estimates. They may not account for site-specific complexities or regional variations in labor costs. Therefore, it’s essential to supplement online calculator results with a consultation from experienced contractors. Contractors conduct on-site assessments, providing more accurate cost estimates that consider project-specific factors. They can identify potential challenges and adjust the estimate accordingly. Getting multiple quotes from different contractors is recommended to ensure you obtain a competitive and fair price.
Sample Budget Template
A well-structured budget template simplifies cost tracking and management. Here’s a sample template:
| Category | Estimated Cost |
|---|---|
| Materials (Steel Siding, Trim, Flashing, Fasteners) | $[Amount] |
| Labor (Installation, Removal of Existing Siding) | $[Amount] |
| Permits and Inspections | $[Amount] |
| Contingency Fund (10-15% of Total) | $[Amount] |
| Total Estimated Cost | $[Amount] |
Remember to fill in the bracketed amounts with your specific project cost estimates. This detailed breakdown ensures transparency and facilitates effective budget management throughout the project lifecycle. Regularly reviewing and updating the budget based on actual expenses ensures that the project stays within the allocated financial limits.
Visual Representation of Cost Factors: Steel Siding Cost

Understanding the cost breakdown of steel siding installation is crucial for accurate budgeting. Visual aids can significantly improve comprehension of the various contributing factors and their relative importance. A well-designed visual representation clarifies the complexities of pricing, enabling homeowners and contractors to make informed decisions.
Cost Component Breakdown Pie Chart
To effectively visualize the relative contribution of different cost components, a pie chart would be ideal. This chart would represent the total cost of the steel siding project as 100%. Each slice of the pie would correspond to a specific cost component, such as materials (steel panels, fasteners, underlayment), labor (installation, preparation, cleanup), permits and inspections, and potentially other miscellaneous expenses like waste removal or site preparation. The size of each slice would be directly proportional to its percentage of the total cost. For example, if materials account for 40% of the total cost, its slice would occupy 40% of the pie chart’s area. This provides a clear, at-a-glance understanding of where the majority of the money is being spent. A legend would clearly label each slice with its corresponding cost component and percentage.
Project Size vs. Total Cost Graph
A scatter plot graph would effectively illustrate the relationship between project size (measured in square footage) and total cost. Each point on the graph would represent a single project, with its x-coordinate representing the project’s size and its y-coordinate representing the total cost. A trend line could be added to the graph to visually represent the overall relationship. This line would show whether the cost increases linearly with project size (a straight line) or at a different rate (a curved line). For instance, a project of 1000 square feet might cost $10,000, while a 2000 square feet project might cost closer to $18,000 rather than $20,000, illustrating potential economies of scale. This visualization helps homeowners understand the cost implications of larger or smaller projects.
Steel Siding Profile and Color Price Comparison Bar Chart
A bar chart would effectively showcase the price differences between various steel siding profiles and colors. The x-axis would list different steel siding profiles (e.g., vertical, horizontal, shake, beaded) and colors (e.g., brown, gray, white, blue). The y-axis would represent the cost per square foot. Each bar would represent the price of a specific profile and color combination. This allows for a quick comparison of the relative costs of different aesthetic choices. For example, a premium color like a deep, custom-mixed shade might be significantly more expensive than a standard color like beige. Similarly, more complex profiles like shake or beaded siding could command higher prices than simpler horizontal panels. This visual aid empowers homeowners to make informed decisions about balancing aesthetics and budget.
Ultimately, the cost of steel siding is a variable equation dependent on numerous interconnected factors. From the initial material selection and regional pricing to the complexities of your home’s structure and the chosen contractor, a thorough understanding of these variables is crucial for accurate budgeting. By carefully considering the information presented here – encompassing material comparisons, installation breakdowns, and budgeting strategies – you can confidently navigate the process and select a steel siding solution that aligns perfectly with your needs and budget. Remember, a well-informed decision is the cornerstone of a successful project.
FAQ Explained
What is the average lifespan of steel siding?
Steel siding boasts an impressive lifespan, typically lasting 30-50 years or more with proper maintenance.
Does steel siding increase home value?
Yes, steel siding is generally considered a valuable upgrade that can increase your home’s resale value due to its durability and low-maintenance nature.
Can I install steel siding myself?
While possible for some DIY enthusiasts with experience, professional installation is highly recommended to ensure proper results and avoid potential warranty issues.
What are the warranty options for steel siding?
Warranty terms vary by manufacturer and type of siding, so it’s crucial to review the specific warranty details before purchasing.
Are there any tax credits or rebates available for steel siding installation?
Tax credits and rebates are location-specific and may vary depending on factors like energy efficiency improvements. Check with your local government agencies for details.









